Communication begins when a sender encodes an idea or thought. This process, known as encoding, is crucial for effective communication, as it involves transforming an idea into a message that can be transmitted and understood by others. Encoding involves various methods, such as verbal, nonverbal, and written communication, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Understanding the process of encoding is essential for effective communication. By carefully selecting the appropriate encoding method and ensuring clarity and accuracy in the message, senders can increase the likelihood of their message being received and interpreted as intended.
Encoding: The Sender’s Role

Encoding is the process of converting an idea or thought into a message that can be transmitted to a receiver. This involves selecting the appropriate words, symbols, or gestures to convey the intended meaning. Encoding can be verbal, nonverbal, or written.
Verbal encoding involves using spoken words to communicate a message. Nonverbal encoding involves using body language, facial expressions, and gestures to convey a message. Written encoding involves using written words to communicate a message.
The effectiveness of communication can be affected by the choice of encoding method. For example, verbal encoding may be more effective for conveying complex ideas, while nonverbal encoding may be more effective for conveying emotions.
Decoding: The Receiver’s Role
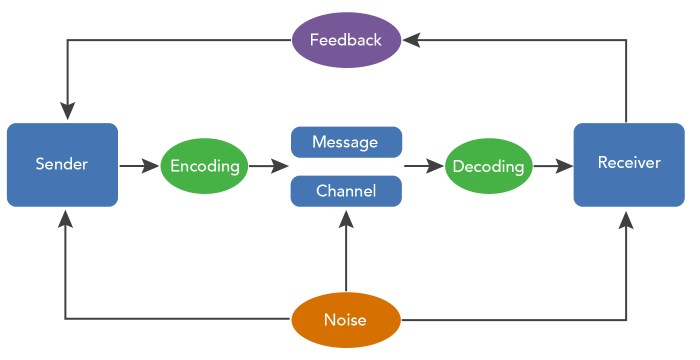
Decoding is the process of interpreting a message and extracting its meaning. This involves understanding the words, symbols, or gestures used in the message and interpreting their intended meaning. Decoding can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as context, culture, and personal experiences.
Context refers to the situation in which the message is communicated. Culture refers to the shared beliefs, values, and norms of a group of people. Personal experiences refer to the individual’s own experiences and knowledge.
Decoding can lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations if the receiver does not have the necessary context, cultural understanding, or personal experiences to correctly interpret the message.
The Communication Channel
The communication channel is the medium through which a message is transmitted from the sender to the receiver. The choice of communication channel can affect the effectiveness of communication.
Different communication channels have different advantages and disadvantages. For example, face-to-face communication allows for immediate feedback and nonverbal cues, while email communication is more convenient and allows for more time to compose a message.
The choice of communication channel should be based on the nature of the message, the relationship between the sender and receiver, and the desired outcome of the communication.
Feedback and Noise: Communication Begins When A Sender Encodes An Idea Or Thought.
Feedback is information that is provided by the receiver to the sender about how the message was received and interpreted. Feedback can be verbal, nonverbal, or written.
Feedback is important because it allows the sender to assess the effectiveness of their communication and make adjustments as needed. Feedback can also help to build rapport between the sender and receiver.
Noise is anything that interferes with the transmission or reception of a message. Noise can be physical, such as background noise, or psychological, such as distractions or biases.
Noise can reduce the effectiveness of communication by making it difficult for the receiver to understand the message.
Context and Culture
Context and culture play a significant role in shaping communication. Context refers to the situation in which the communication occurs, while culture refers to the shared beliefs, values, and norms of a group of people.
Context can influence the meaning of a message. For example, the same words can have different meanings depending on the context in which they are used.
Culture can also influence the meaning of a message. For example, the same gesture can have different meanings in different cultures.
It is important to be aware of the context and culture in which communication is occurring in order to avoid misunderstandings.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of encoding in communication?
Encoding in communication serves to transform an idea or thought into a message that can be transmitted and understood by others.
What are the different methods of encoding used in communication?
Encoding methods include verbal communication (spoken words), nonverbal communication (body language, gestures), and written communication (text, symbols).
How does the choice of encoding method affect communication effectiveness?
The choice of encoding method can influence the clarity, accuracy, and impact of the message, affecting its overall effectiveness.